Career Counseling
John Krumboltz posits a theory of career counseling that stresses social learning as its key ingredient. He says that 'People with differing genetic characteristics are exposed to infinitely varied learning opportunities (or lack therof) as a result of the social, cultural, and economic circumstances that exist at the time and place where they live. The consequences of these learning experiences are synthesized by each individual…(to) guide each person's thinking about appropriate career decisions and actions.' (1996, p.60).
Related posts: Donald Super Career Counseling Theory Donald Super created a useful framework for conceptualizing the constantly evolving nature of career development. The theory presents the career process as one in which a person is confronted with various stages that he or she must undergo and complete before moving on to the next stage. According to Anne Roe's personality theory of career choice, people choose occupational fields based on their , which were influenced by the childhood environments that they experienced. Parent's occupation C. Need structures D. Attachment to their parental figure 10.
Krumboltz, Ph.D., has demonstrated throughout his life and work that counselors can help clients with career, academic, and personal problems to explore and expand their learning experiences; challenge unhelpful beliefs; embrace unanticipated opportunities; and take positive actions to create more satisfying lives for themselves. He received from the American Psychological Association.
Whatever your personal beliefs about whether personality traits are genetic or products of environmental conditions, his theoretical formulations work extremely well within a cognitive behavioral framework. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is probably the most well-known therapy among laypeople. It was developed from the philosophy of the Stoics, a sect of ancient Greeks, and stresses that how we perceive an event is actually what causes a reaction, not the event itself. Most people think in terms of cause and effect. Visually, cause and effect would look like this:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy places the emphasis on a middle stage that predicts those consequences. Visually, it looks like this:
Much of the work in CBT revolves around addressing and challenging all kinds of faulty thinking that can lead to dysfunction. Let's use an example to flesh this out. Imagine that you have just transferred to a new high school and people have not been friendly to you on your first day. You walk into the cafeteria at lunch and see a group of people who you assume are the popular kids. A few of them look in your direction, turn back to the group and make a few comments that you cannot hear, and then everyone breaks into uproarious laughter. Blood rushes to your face, adrenaline starts pumping through your body, you feel humiliated and angry, and resolve not to speak to any of them. You leave the cafeteria feeling angry, embarrassed, and that your self-esteem has been damaged.

In this example you are thinking and acting in terms of cause and effect. The activating event of people laughing causes you to feel humiliated and triggers many bodily reactions such as higher blood pressure, a rush of adrenaline, and a sick feeling in your stomach. However, how can you be certain that they were laughing at you? Even if they were, why should it effect your self-esteem when they do not even know you?
It is overwhelming to think about all of the ways that our faulty thinking and skewed perception of events can influence our lives. One person gets made fun of and brushes it off as nothing to worry about. The next feels angry and the need to get even. The next feels sad and symptoms of depression for a few days. Objectively the same activating event occurs, but this event has profoundly different ramifications based upon how each person views it.

Krumboltz (1994) lists some of the ways that people engage in faulty thinking that limits their career development. These include:
1. A lack of recognition that changes could happen
Anne Roe Career Development Theory Pdf Creator Online
2. Eliminating alternatives for inappropriate reasons
Anne Roe Career Development Theory
3. Viewing life in negative terms
4. Blaming others
5. Repeatedly saying 'I can't' sometimes accompanied by negative feelings of depression and/or anxiety
As you can probably see, CBT along with Kruboltz's career theory and tests like the Career Beliefs Inventory can be a powerful way for you to see your career process and your life in a new light.
Related posts:
- Donald Super Career Counseling Theory Donald Super created a useful framework for conceptualizing the constantly evolving nature of career development. The theory presents the career process as one in which a person is confronted with various stages that he or she must undergo and complete before moving on to the next stage. This theory, which will be explained below, is […]..
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Explained Cognitive behavioral therapy doesn't discount the power or importance of the emotional apparatus in human life but it does choose to put the emphasis on cognition, on challenging and correcting faulty thinking patterns, in order to effect therapeutic change. In this sense from the CBT point of view the way you feel is a direct […]..
- Use Your Newfound Insight To Change The Practice Of Your Life A lasting effect of the psychoanalytic tradition on the common understanding of how therapy works is that increasing insight leads to cure. The idea in psychoanalysis was that bringing unconscious drives, motivations, and other hidden material into conscious awareness was the endgame, the way to eradicate neurosis. The problem though, and the various therapeutic paradigms […]..
- Four Noble Truths In his book ‘To Have or To Be' Erich Fromm proposes a variation on the four noble truths taught by the Buddha. We will list them below and then discuss their relevance to the counseling process. 1. We are suffering and are aware that we are. 2. We recognize the origin of our ill-being. 3. […]..
- Depression CBT A proven model for helping people overcome depression is cognitive restructuring using cognitive behavioral therapy. We will discuss some of the philosophical components for treatment using CBT and the practical application of its principles. Aaron Beck, the creator of CBT, discovered in his work with patients that whether they were consciously aware of the fact […]..
- Emotional Bank Account The psychologist John Gottman has an interesting metaphor to explain why some couples thrive while others disintegrate. He calls it the emotional bank account. Think of positive, relationship affirming interactions as deposits that are made intermittently and stored up for a rainy day. When a bump in the road invariably comes along, the overall feelings […]..
- Do Not Punish The Wrong People For What Happens To You When our plans are thwarted or we feel diminished in some way, many of us find ourselves in the uncomfortable position of having a lot of negative energy to unload but not feeling able to direct it towards the correct person due an imbalance of power. So we punish the wrong people, usually those closest […]..
- Overcoming Impatience Good therapists are always skeptical of and make sure to challenge comments like 'He makes me so angry,' 'She gets under my skin,' or 'He makes me lose my patience.' People who think this way see the world and their relationships in terms of cause and effect, action and reaction, neglecting the vital intermediate stage […]..
- Ulterior Motives Lots of the time a person seems to convey one idea but is actually trying to make you take away a different point entirely. With practice it's easy to delve below the surface and understand many of the ulterior motives of those around us. But in order to do it we need to understand what […]..
- Productive Work It was Erich Fromm who believed that love and productive work were the two most essential elements for mental health and happiness. If you're like a lot of people you'll readily agree with love being important but might scoff at the idea of giving work equal billing, even going so far as to say that […]..
- Now I saw someone repost an article I did called ‘Path of Mastery' with the added comment ‘Path TO Mastery' and smiled to myself because I chose the title quite purposefully. Actually the insistence on using the preposition ‘to' is indicative of how most of us in the West think about life, and changing our mentalities […]..
- Make A List Of Five Things You Want Your Partner To Do If You Die This article is especially relevant for couples nearing the end of their lifespans, where one partner will leave the other behind to try to move forward without the anchor that has offered support for so many years. But it's a good exercise for anybody, a chance to strengthen your relationship by putting ephemeral hopes and […]..
- Choosing The Right Career Path It's a fact that many people who choose their own career paths don't have much passion for or even interest in what they do for a living. The most important psychological reason why is that societal forces are powerful, all too powerful. They usually have more say over conscious thought and intention than our own […]..
- Career Diamond Most people come to career counseling with the hope that they will be able to take a few tests, narrow possible career options, and be given a neat answer for the career and specific job that fits them best. In a general sense, anxiety is usually prevalent in times of uncertainty. It makes sense that […]..
- Telling Your Story As The Expert Most therapists, regardless of the psychological theories they use, consider themselves to be experts, and rightfully so. The problem with this attitude is that as experts they feel that they are the ones with the access to the knowledge and wisdom that will help their clients improve. The role of the client in this context […]..
- Why It Is Never Too Late To Follow A New Career Path As we have already written, one of the most common reasons out there for not pursuing a desired career path is advanced age. The feeling is that the time has passed, that it would have been nice but it just isn't practical now. There's a wonderfully practical way to refute this argument, and it's that […]..
- Why So Serious In Counseling People thinking about going to counseling often have a preconceived notion that the therapy process will be a grim and serious endeavor. Actually many counselors cultivate the image and probably do spend the majority of sessions straight faced and inhabiting a role of what they believe to be professional. One of the popular refrains I […]..
- Changes In Perception During Counseling I had a friend recently ask me if there were any commonalities in how clients perceive counseling sessions as they progress, and I didn't have to think too hard about it because most go through the same basic sequence of stages. If you are currently in counseling or considering going it will be useful for […]..
- Mindful Counseling There is often a dissimilarity in expectations between medical treatment and mental health treatment. One of the reasons is probably because psychology and counseling are more ephemeral. You can't touch or see psychological ideas. And sometimes improvements happen without anyone really knowing how or why. Erich Fromm wrote about how when people seek medical help […]..
- Transformation In Counseling As a counselor, if you aren't conscious of the unconscious pull your clients feel to use you as a garbage receptacle for unwanted, uncomfortable, dangerous thoughts and feelings you're going to run into problems because you and your clients will live two different realities during counseling exchanges. You're trained to appreciate the communication of private […]..
Anne Roe (1904—1991) was born and raised in Denver, Colorado. Upon graduating from the University of Denver, she attended Columbia University, following the recommendation of Thomas Garth. At Columbia, Roe worked in the office of Edward Lee Thorndike, graduating with her Ph.D. in experimental psychology under the supervision of Robert S. Woodworth. The publication of The Psychology of Occupations would introduce Roe's theory of personality development and career choice, her most enduring scientific contribution.
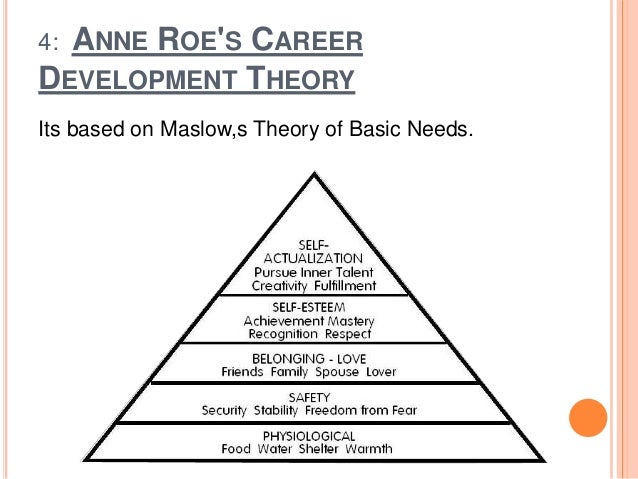
Roe's theory can be separated into two key areas: theoretical aspects of personality and classification of occupations. Inspired by Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Roe incorporated the psychological needs that develop out of parent-child interactions in her conceptualization of personality. Roe classified parent-child interaction patterns into three categories, each with two subcategories: (1) emotional concentration on the child, further classified as being overprotective or overdemanding, (2) avoidance of the child, further classified as emotional rejection or neglect, and (3) acceptance of the child, further classified as casual or loving. Roe's interest in parent-child interactions led to the development of the Parent-Child Relations Questionnaire and its revision as a means of accurately assessing such interactions. Out of parent-child interactions, Roe thought that children went on to develop an orientation either toward or not toward people.
Anne Roe Career Development Theory Pdf Creator Software
Roe was dissatisfied with existing classification systems for occupations, including the benchmark Dictionary of Occupational Titles. In order to compare the individual to a full spectrum of occupations, Roe set out to develop a comprehensive classification system that would allow her to engage her inquiry. The result was a two-dimensional, eight by six classification system with eight categories of occupations (service, business contact, organization, technology, outdoor, science, general culture, and arts and entertainment) and six levels (professional and managerial, levels 1 and 2; semiprofessional and small business, level 3; skilled, level 4; semiskilled, level 5; and unskilled, level 6) within each category.
Research into the impact of parent-child interactions on career choice has not resulted in significant support for Roe's theory. Concerns with subject recall of parent-child interactions, differences in parenting styles between parents and over time, and sample sizes, among other issues, have been cited. Roe openly acknowledged the criticisms of her theory and expressed concerns that her classification system did not adequately address the experiences of women and minorities. In addition, Roe stated that her theory was developed with little forethought in regard to its application. Still, research support can be found for Roe's classification system, and a minimal amount of support has been found related to the impact of early interactions upon the work-related behaviors and activities within certain areas of occupational specialization. The impact of Roe's theory has been realized across the various facets of activities of career development professionals such as teaching, counseling, placement, and research. Roe's classification system has proven particularly useful to career counselors in the influence it has had in the development of career assessment instruments and in its overall contribution to the mapping of the world of work.
References:

In this example you are thinking and acting in terms of cause and effect. The activating event of people laughing causes you to feel humiliated and triggers many bodily reactions such as higher blood pressure, a rush of adrenaline, and a sick feeling in your stomach. However, how can you be certain that they were laughing at you? Even if they were, why should it effect your self-esteem when they do not even know you?
It is overwhelming to think about all of the ways that our faulty thinking and skewed perception of events can influence our lives. One person gets made fun of and brushes it off as nothing to worry about. The next feels angry and the need to get even. The next feels sad and symptoms of depression for a few days. Objectively the same activating event occurs, but this event has profoundly different ramifications based upon how each person views it.
Krumboltz (1994) lists some of the ways that people engage in faulty thinking that limits their career development. These include:
1. A lack of recognition that changes could happen
Anne Roe Career Development Theory Pdf Creator Online
2. Eliminating alternatives for inappropriate reasons
Anne Roe Career Development Theory
3. Viewing life in negative terms
4. Blaming others
5. Repeatedly saying 'I can't' sometimes accompanied by negative feelings of depression and/or anxiety
As you can probably see, CBT along with Kruboltz's career theory and tests like the Career Beliefs Inventory can be a powerful way for you to see your career process and your life in a new light.
Related posts:
- Donald Super Career Counseling Theory Donald Super created a useful framework for conceptualizing the constantly evolving nature of career development. The theory presents the career process as one in which a person is confronted with various stages that he or she must undergo and complete before moving on to the next stage. This theory, which will be explained below, is […]..
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Explained Cognitive behavioral therapy doesn't discount the power or importance of the emotional apparatus in human life but it does choose to put the emphasis on cognition, on challenging and correcting faulty thinking patterns, in order to effect therapeutic change. In this sense from the CBT point of view the way you feel is a direct […]..
- Use Your Newfound Insight To Change The Practice Of Your Life A lasting effect of the psychoanalytic tradition on the common understanding of how therapy works is that increasing insight leads to cure. The idea in psychoanalysis was that bringing unconscious drives, motivations, and other hidden material into conscious awareness was the endgame, the way to eradicate neurosis. The problem though, and the various therapeutic paradigms […]..
- Four Noble Truths In his book ‘To Have or To Be' Erich Fromm proposes a variation on the four noble truths taught by the Buddha. We will list them below and then discuss their relevance to the counseling process. 1. We are suffering and are aware that we are. 2. We recognize the origin of our ill-being. 3. […]..
- Depression CBT A proven model for helping people overcome depression is cognitive restructuring using cognitive behavioral therapy. We will discuss some of the philosophical components for treatment using CBT and the practical application of its principles. Aaron Beck, the creator of CBT, discovered in his work with patients that whether they were consciously aware of the fact […]..
- Emotional Bank Account The psychologist John Gottman has an interesting metaphor to explain why some couples thrive while others disintegrate. He calls it the emotional bank account. Think of positive, relationship affirming interactions as deposits that are made intermittently and stored up for a rainy day. When a bump in the road invariably comes along, the overall feelings […]..
- Do Not Punish The Wrong People For What Happens To You When our plans are thwarted or we feel diminished in some way, many of us find ourselves in the uncomfortable position of having a lot of negative energy to unload but not feeling able to direct it towards the correct person due an imbalance of power. So we punish the wrong people, usually those closest […]..
- Overcoming Impatience Good therapists are always skeptical of and make sure to challenge comments like 'He makes me so angry,' 'She gets under my skin,' or 'He makes me lose my patience.' People who think this way see the world and their relationships in terms of cause and effect, action and reaction, neglecting the vital intermediate stage […]..
- Ulterior Motives Lots of the time a person seems to convey one idea but is actually trying to make you take away a different point entirely. With practice it's easy to delve below the surface and understand many of the ulterior motives of those around us. But in order to do it we need to understand what […]..
- Productive Work It was Erich Fromm who believed that love and productive work were the two most essential elements for mental health and happiness. If you're like a lot of people you'll readily agree with love being important but might scoff at the idea of giving work equal billing, even going so far as to say that […]..
- Now I saw someone repost an article I did called ‘Path of Mastery' with the added comment ‘Path TO Mastery' and smiled to myself because I chose the title quite purposefully. Actually the insistence on using the preposition ‘to' is indicative of how most of us in the West think about life, and changing our mentalities […]..
- Make A List Of Five Things You Want Your Partner To Do If You Die This article is especially relevant for couples nearing the end of their lifespans, where one partner will leave the other behind to try to move forward without the anchor that has offered support for so many years. But it's a good exercise for anybody, a chance to strengthen your relationship by putting ephemeral hopes and […]..
- Choosing The Right Career Path It's a fact that many people who choose their own career paths don't have much passion for or even interest in what they do for a living. The most important psychological reason why is that societal forces are powerful, all too powerful. They usually have more say over conscious thought and intention than our own […]..
- Career Diamond Most people come to career counseling with the hope that they will be able to take a few tests, narrow possible career options, and be given a neat answer for the career and specific job that fits them best. In a general sense, anxiety is usually prevalent in times of uncertainty. It makes sense that […]..
- Telling Your Story As The Expert Most therapists, regardless of the psychological theories they use, consider themselves to be experts, and rightfully so. The problem with this attitude is that as experts they feel that they are the ones with the access to the knowledge and wisdom that will help their clients improve. The role of the client in this context […]..
- Why It Is Never Too Late To Follow A New Career Path As we have already written, one of the most common reasons out there for not pursuing a desired career path is advanced age. The feeling is that the time has passed, that it would have been nice but it just isn't practical now. There's a wonderfully practical way to refute this argument, and it's that […]..
- Why So Serious In Counseling People thinking about going to counseling often have a preconceived notion that the therapy process will be a grim and serious endeavor. Actually many counselors cultivate the image and probably do spend the majority of sessions straight faced and inhabiting a role of what they believe to be professional. One of the popular refrains I […]..
- Changes In Perception During Counseling I had a friend recently ask me if there were any commonalities in how clients perceive counseling sessions as they progress, and I didn't have to think too hard about it because most go through the same basic sequence of stages. If you are currently in counseling or considering going it will be useful for […]..
- Mindful Counseling There is often a dissimilarity in expectations between medical treatment and mental health treatment. One of the reasons is probably because psychology and counseling are more ephemeral. You can't touch or see psychological ideas. And sometimes improvements happen without anyone really knowing how or why. Erich Fromm wrote about how when people seek medical help […]..
- Transformation In Counseling As a counselor, if you aren't conscious of the unconscious pull your clients feel to use you as a garbage receptacle for unwanted, uncomfortable, dangerous thoughts and feelings you're going to run into problems because you and your clients will live two different realities during counseling exchanges. You're trained to appreciate the communication of private […]..
Anne Roe (1904—1991) was born and raised in Denver, Colorado. Upon graduating from the University of Denver, she attended Columbia University, following the recommendation of Thomas Garth. At Columbia, Roe worked in the office of Edward Lee Thorndike, graduating with her Ph.D. in experimental psychology under the supervision of Robert S. Woodworth. The publication of The Psychology of Occupations would introduce Roe's theory of personality development and career choice, her most enduring scientific contribution.
Roe's theory can be separated into two key areas: theoretical aspects of personality and classification of occupations. Inspired by Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Roe incorporated the psychological needs that develop out of parent-child interactions in her conceptualization of personality. Roe classified parent-child interaction patterns into three categories, each with two subcategories: (1) emotional concentration on the child, further classified as being overprotective or overdemanding, (2) avoidance of the child, further classified as emotional rejection or neglect, and (3) acceptance of the child, further classified as casual or loving. Roe's interest in parent-child interactions led to the development of the Parent-Child Relations Questionnaire and its revision as a means of accurately assessing such interactions. Out of parent-child interactions, Roe thought that children went on to develop an orientation either toward or not toward people.
Anne Roe Career Development Theory Pdf Creator Software
Roe was dissatisfied with existing classification systems for occupations, including the benchmark Dictionary of Occupational Titles. In order to compare the individual to a full spectrum of occupations, Roe set out to develop a comprehensive classification system that would allow her to engage her inquiry. The result was a two-dimensional, eight by six classification system with eight categories of occupations (service, business contact, organization, technology, outdoor, science, general culture, and arts and entertainment) and six levels (professional and managerial, levels 1 and 2; semiprofessional and small business, level 3; skilled, level 4; semiskilled, level 5; and unskilled, level 6) within each category.
Research into the impact of parent-child interactions on career choice has not resulted in significant support for Roe's theory. Concerns with subject recall of parent-child interactions, differences in parenting styles between parents and over time, and sample sizes, among other issues, have been cited. Roe openly acknowledged the criticisms of her theory and expressed concerns that her classification system did not adequately address the experiences of women and minorities. In addition, Roe stated that her theory was developed with little forethought in regard to its application. Still, research support can be found for Roe's classification system, and a minimal amount of support has been found related to the impact of early interactions upon the work-related behaviors and activities within certain areas of occupational specialization. The impact of Roe's theory has been realized across the various facets of activities of career development professionals such as teaching, counseling, placement, and research. Roe's classification system has proven particularly useful to career counselors in the influence it has had in the development of career assessment instruments and in its overall contribution to the mapping of the world of work.
References:
- Osipow, S. H., & Fitzgerald, L. F. (1996). Theories of career development (4th ed.). Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
- Roe, A. (1956). The psychology of occupations. New York: Wiley.
- Roe, A. (1957). Early determinants of vocational choice. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 4, 212-217.
- Roe, A., & Lunneborg, P. W. (1990). Personality development and career choice. In D. Brown & L. Brooks (Eds.), Career choice and development: Applying contemporary theories to practice (2nd ed., pp. 68-101). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
- Tinsley, H. E. A. (Ed.). (1997). [Special section on Anne Roe]. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 51, 280-318.
